by Dr. Anna Blume
Professor of the History of Art Fashion Institute of Technology State University of New York November 2019.
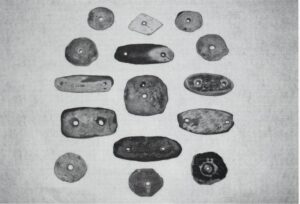
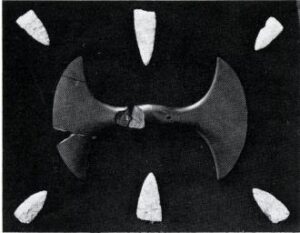
Photographing bannerstones can reveal their shapes, surfaces, and conditions and can also engage both photographer and viewer in a meaningful relationship to these complex carved stones. In the fall of 2016 and spring of 2017, I selected and photographed 61 of 472 bannestones in the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) collection. I chose these 61 stones based on how well they represented the range of materials that Archaic sculptors chose, the twenty-four types of bannerstones, and the various conditions of bannerstones within the collection. 580 photographs from that study are available for review and download on this ABP website. Based on my experience looking at these stones and thinking of ways to represent their materials, morphology, and current conditions, I have devised a set of recommendations for future scholars and museum photographers to consider when photographing bannerstones.
Note: For all images taken in the AMNH, I used a Canon 7D with a Canon Macro EF 100mm f/2.8 Macro lens (with the cropped sensor of the 7D this was the equivalent of a 160mm lens). Given the varying angles that I took of each bannerstone, I chose to hand hold the camera instead of placing it on a tripod. With high voltage strobe lighting, I could choose f-stop and aperture settings that were optimum without a tripod.[1]
Fullscreen Mode